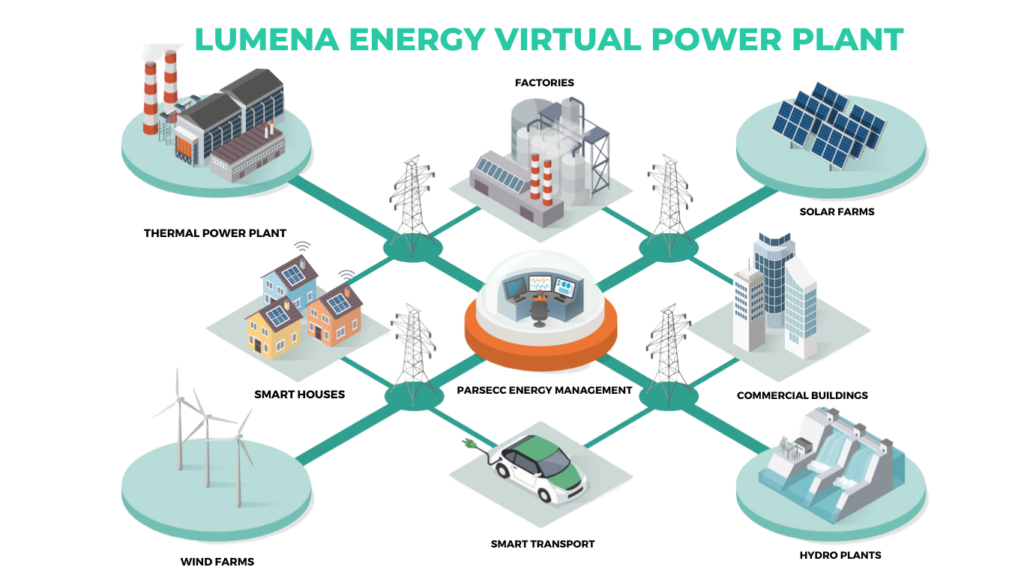
What Is A Virtual Power Plant?


Virtual power plants (VPPs) are a way of using a network of distributed renewable energy sources, such as solar panels and wind turbines, to generate electricity. These renewable energy sources are often located in different places and connected to the grid through a central control system, which allows them to operate as a single, large power plant.
The use of VPPs has increased in recent years as more and more people and businesses are looking to use renewable energy sources. One of the main advantages of VPPs is that they can provide a more reliable and consistent supply of electricity than a single power plant. This is because the network of renewable energy sources can compensate for fluctuations in the output of individual sources, such as when the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing.
VPPs also offer a number of environmental benefits. Because they use renewable energy sources, VPPs can help reduce our reliance on fossil fuels and the greenhouse gas emissions that come with them. In addition, VPPs can help to distribute renewable energy more evenly across a grid, which can help to reduce the need for expensive and environmentally damaging transmission lines.
Another advantage of VPPs is that they can be more cost-effective than traditional power plants. Because renewable energy sources are often available at little or no cost, VPPs can help to lower electricity prices for consumers. In addition, VPPs can help to reduce the need for expensive backup power sources, such as natural gas plants, which are typically used to provide electricity when demand is high or renewable energy sources are not available.
Overall, VPPs offer a number of benefits over traditional power plants and can help to accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and reliable electricity grid. As more and more people and businesses turn to renewable energy sources, VPPs will play an increasingly important role in the future of our energy system.

Responses